Chief Buffalo Picture Search: Busted Again
March 12, 2016
By Amorin Mello
This post is one of several that seek to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, please read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
Posts on Chequamegon History are generally of the obscure variety and are probably only interesting to a handful of people. We anticipate this one could cause some controversy as it concerns an object that holds a lot of importance to many people who live in our area. All we can say about that is that this post represents our research into original historical documents. We did not set out to prove anybody right or wrong, and we don’t think this has to be the last word on the subject. This post is simply our reasoned conclusions based on the evidence we’ve seen. Take from it what you will.

“Chippewa man in Washington, D.C.”
Carte de visite by Charles D. Fredricks & Co., 1862
10 cm x 6 cm
From the Charles W. Jenks carte de visite collection
Photo. 126.194
~ Massachusetts Historical Society Collections Online
The above image has been shared on Facebook and Pinterest social media networks as a photograph of Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. Evidently, it originally came from the Massachusetts Historical Society, and was labeled as an unidentified Chippewa man in Washington D.C. However, it is dated as 1862, which was several years after the death of Chief Buffalo from La Pointe.
On the other hand… it was pointed out to me that the person in the above photograph bears a strong resemblance to a certain painting of Chief Buffalo publicly available for viewing in the main lobby of the Tribal Administration Building in Red Cliff (or here, for convenience). The artist of this modern painting is a living member of Chief Buffalo’s family, is a tribal member of the Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa, and has attributed the painting’s appearance to two busts of Chief Buffalo found in Washington D.C.
These inspiring busts were featured previously in Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Capital Busts, by Leo Filipczak, and are summarized with the three following images:

Be sheekee, or Buffalo by Francis Vincenti, Marble, Modeled 1855, Carved 1856 (United States Senate)
Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.

Be Sheekee: A Chippewa Warrior from the Sources of the Mississippi, bronze, by Joseph Lassalle after Francis Vincenti, House wing of the United States Capitol (U.S. Capitol Historical Society).
Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.

Be-She-Kee (Buffalo), Head Chief of the Leech Lake Chippewas c. 1863 (Whitney’s Gallery, St. Paul)
Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.
Unfortunately, we are not any closer to finding a photograph of Chief Buffalo from La Pointe.
The good news is:
The photograph in question can safely be identified as Chief Buffalo… from Leech Lake.

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.
Error Correction: Photo Mystery Still Unsolved
April 27, 2014

According to Benjamin Armstrong, the men in this photo are (back row L to R) Armstrong, Aamoons, Giishkitawag, Ba-quas (identified from other photos as Akiwenzii), Edawi-giizhig, O-be-quot, Zhingwaakoons, (front row L to R) Jechiikwii’o, Naaganab, and Omizhinawe in an 1862 delegation to President Lincoln. However, Jechiikwii’o (Jayjigwyong) died in 1860.
In the Photos, Photos, Photos post of February 10th, I announced a breakthrough in the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search. It concerned this well-known image of “Chief Buffalo.”

(Wisconsin Historical Society)
The image, long identified with Gichi-weshkii, also called Bizhiki or Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855, has also been linked to the great chief’s son and grandson. In the February post, I used Benjamin Armstrong’s description of the following photo to conclude that the man seated on the left in this group photograph was in fact the man in the portrait. That man was identified as Jechiikwii’o, the oldest son of Chief Buffalo (a chief in his own right who was often referred to as Young Buffalo).

Another error in the February post is the claim that this photo was modified for and engraving in Armstrong’s book, Early Life Among the Indians. In fact, the engraving is derived from a very similar photo seen at the top of this post (Minnesota Historical Society).

(Marr & Richards Co. for Armstrong)
The problem with this conclusion is that it would have been impossible for Jechiikwii’o to visit Lincoln in the White House. The sixteenth president was elected shortly after the following report came from the Red Cliff Agency:

Drew, C.K. Report on the Chippewas of Lake Superior. Red Cliff Agency. 29 Oct. 1860. Pg. 51 of Annual Report of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs. Bureau of Indian Affairs. 1860. (Digitized by Google Books).
This was a careless oversight on my part, considering this snippet originally appeared on Chequamegon History back in November. Jechiikwii’o is still a likely suspect for the man in the photo, but this discrepancy must be settled before we can declare the mystery solved.
The question comes down to where Armstrong made the mistake. Is the man someone other than Jechiikwii’o, or is the photo somewhere other than the Lincoln White House?
If it isn’t Jechiikwii’o, the most likely candidate would be his son, Antoine Buffalo. If you remember this post, Hamilton Ross did identify the single portrait as a grandson of Chief Buffalo. Jechiikwii’o, a Catholic, gave his sons Catholic names: Antoine, Jean-Baptiste, Henry. Ultimately, however, they and their descendants would carry their grandfather’s name as a surname: Antoine Buffalo, John Buffalo, Henry Besheke, etc., so one would expect Armstrong (who was married into the family) to identify Antoine as such, and not by his father’s name.
However, I was recently sent a roster of La Pointe residents involved in stopping the whiskey trade during the 1855 annuity payment. Among the names we see:
…Antoine Ga Ge Go Yoc
John Ga Ge Go Yoc…[Read the first two Gs softly and consider that “Jayjigwyong” was Leonard Wheeler’s spelling of Jechiikwii’o]
So, Antoine and John did carry their father’s name for a time.
Regardless, though, the age and stature of the man in the group photograph, Armstrong’s accuracy in remembering the other chiefs, and the fact that Armstrong was married into the Buffalo family still suggest it’s Jechiikwii’o in the picture.
Fortunately, there are enough manuscript archives out there related to the 1862 delegation that in time I am confident someone can find the names of all the chiefs who met with Lincoln. This should render any further speculation irrelevant and will hopefully settle the question once and for all.
Until then, though, we have to reflect again on why Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians is simultaneously the most accurate and least accurate source on the history of this area. It must be remembered that Armstrong himself admitted his memory was fuzzy when he dictated the work in his final years. Still, the level of accuracy in the small details is unsurpassed and confirms his authenticity even as the large details can be way off the mark.
Thank you to Charles Lippert for providing the long awaited translation and transliteration of Jechiikwii’o into the modern Ojibwe alphabet. Amorin Mello kindly shared the 1855 La Pointe documents, transcribed and submitted to the Michigan Family History website by Patricia Hamp, and Travis Armstrong’s ChiefBuffalo.com remains an outstanding bank of primary sources on the Buffalo and Armstrong families.
Photos, Photos, Photos
February 10, 2014
The queue of Chequamegon History posts that need to be written grows much faster than my ability to write them. Lately, I’ve been backed up with mysteries surrounding a number of photographs. Many of these photos are from after 1860, so they are technically outside the scope of this website (though they involve people who were important in the pre-1860 era too.
Photograph posts are some of the hardest to write, so I decided to just run through all of them together with minimal commentary other than that needed to resolve the unanswered questions. I will link all the photos back to their sources where their full descriptions can be found. Here it goes, stream-of-consciousness style:

Ojibwa Delegation by C.M. Bell. Washington D.C. 1880 (NMAI Collections)
This whole topic started with a photo of a delegation of Lake Superior Ojibwe chiefs that sits on the windowsill of the Bayfield Public Library. Even though it is clearly after 1860, some of the names in the caption: Oshogay, George Warren, and Vincent Roy Jr. caught my attention. These men, looking past their prime, were all involved in the politics of the 1850s that I had been studying, so I wanted to find out more about the picture.
As I mentioned in the Oshogay post, this photo is also part of the digital collections of the Smithsonian, but the people are identified by different names. According to the Smithsonian, the picture was taken in Washington in 1880 by the photographer C.M. Bell.
I found a second version of this photo as well. If it wasn’t for one of the chiefs in front, you’d think it was the same picture:
Chippewa Delegation (Denver Public Library Digital Collections)
While my heart wanted to believe the person, probably in the early 20th century, who labelled the Bayfield photograph, my head told me the photographer probably wouldn’t have known anything about the people of Lake Superior, and therefore could only have gotten the chiefs’ names directly from them. Plus, Bell took individual photos:

Edawigijig (Edawi-giizhig “Both Sides of the Sky”), Bad River chief and signer of the Treaty of 1854 (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections)

Niizhogiizhig: “Second Day,” (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections)

Kiskitawag (Giishkitawag: “Cut Ear”) signed multiple treaties as a warrior of the Ontonagon Band but afterwards was associated with the Bad River Band (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections).
By cross-referencing the individual photos with the names listed with the group photo, you can identify nine of the thirteen men. They are chiefs from Bad River, Lac Courte Oreilles, and Lac du Flambeau.
 According to this, the man identified by the library caption as Vincent Roy Jr., was in fact Ogimaagiizhig (Sky Chief). He does have a resemblance to Roy, so I’ll forgive whoever it was, even if it means having to go back and correct my Vincent Roy post:
According to this, the man identified by the library caption as Vincent Roy Jr., was in fact Ogimaagiizhig (Sky Chief). He does have a resemblance to Roy, so I’ll forgive whoever it was, even if it means having to go back and correct my Vincent Roy post:

Vincent Roy Jr. From C. Verwyst’s Life and Labors of Rt. Rev. Frederic Baraga, First Bishop of Marquette, Mich: To which are Added Short Sketches of the Lives and Labors of Other Indian Missionaries of the Northwest (Digitized by Google Books)

Top: Frank Roy, Vincent Roy, E. Roussin, Old Frank D.o., Bottom: Peter Roy, Jos. Gourneau (Gurnoe), D. Geo. Morrison. The photo is labelled Chippewa Treaty in Washington 1845 by the St. Louis Hist. Lib and Douglas County Museum, but if it is in fact in Washington, it was probably the Bois Forte Treaty of 1866, where these men acted as conductors and interpreters (Digitized by Mary E. Carlson for The Sawmill Community at Roy’s Point).
So now that we know who went on the 1880 trip, it begs the question of why they went. The records I’ve found haven’t been overly clear, but it appears that it involved a bill in the senate for “severalty” of the Ojibwe reservations in Wisconsin. A precursor to the 1888 Allotment Act of Senator Henry Dawes, this legislation was proposed by Senator Thaddeus C. Pound of Wisconsin. It would divide the reservations into parcels for individual families and sell the remaining lands to the government, thereby greatly reducing the size of the reservations and opening the lands up for logging.
Pound spent a lot of time on Indian issues and while he isn’t as well known as Dawes or as Richard Henry Pratt the founder of the Carlisle Indian School, he probably should be. Pound was a friend of Pratt’s and an early advocate of boarding schools as a way to destroy Native cultures as a way to uplift Native peoples.
I’m sure that Pound’s legislation was all written solely with the welfare of the Ojibwe in mind, and it had nothing to do with the fact that he was a wealthy lumber baron from Chippewa Falls who was advocating damming the Chippewa River (and flooding Lac Courte Oreilles decades before it actually happened). All sarcasm aside, if any American Indian Studies students need a thesis topic, or if any L.C.O. band members need a new dartboard cover, I highly recommend targeting Senator Pound.
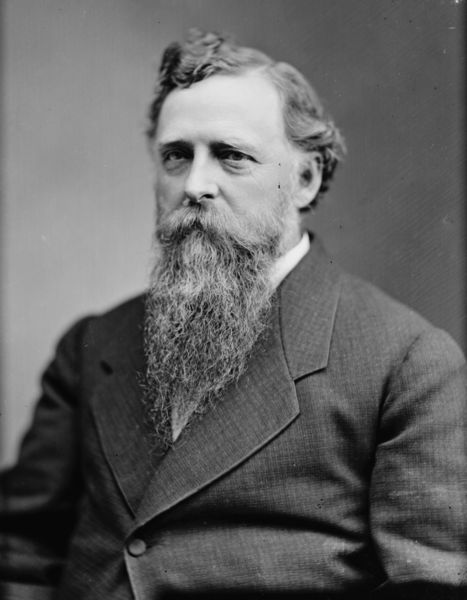

Like many self-proclaimed “Friends of the Indian” in the 1880s, Senator Thaddeus C. Pound of Wisconsin thought the government should be friendly to Indians by taking away more of their land and culture. That he stood to make a boatload of money out of it was just a bonus (Brady & Handy: Wikimedia Commons).
While we know Pound’s motivations, it doesn’t explain why the chiefs came to Washington. According to the Indian Agent at Bayfield they were brought in to support the legislation. We also know they toured Carlisle and visited the Ojibwe students there. There are a number of potential explanations, but without having the chiefs’ side of the story, I hesitate to speculate. However, it does explain the photograph.
Now, let’s look at what a couple of these men looked like two decades earlier:

This stereocard of Giishkitawag was produced in the early 1870s, but the original photo was probably taken in the early 1860s (Denver Public Library).

By the mid 1850s, Akiwenzii (Old Man) was the most prominent chief of the Lac Courte Oreilles Band. This stereocard was made by Whitney and Zimmerman c.1870 from an original possibly by James E. Martin in the late 1850s or early 1860s (Denver Public Library).
Giishkitawag and Akiwenzii are seem to have aged quite a bit between the early 1860s, when these photos were taken, and 1880 but they are still easily recognized. The earlier photos were taken in St. Paul by the photographers Joel E. Whitney and James E. Martin. Their galleries, especially after Whitney partnered with Charles Zimmerman, produced hundreds of these images on cards and stereoviews for an American public anxious to see real images of Indian leaders.
Giishkitawag and Akiwenzii were not the only Lake Superior chiefs to end up on these souvenirs. Aamoons (Little Bee), of Lac du Flambeau appears to have been a popular subject:

Aamoons (Little Bee) was a prominent chief from Lac du Flambeau (Denver Public Library).
As the images were reproduced throughout the 1870s, it appears the studios stopped caring who the photos were actually depicting:
One wonders what the greater insult to Aamoons was: reducing him to being simply “Chippewa Brave” as Whitney and Zimmerman did here, or completely misidentifying him as Na-gun-ub (Naaganab) as a later stereo reproduction as W. M. McLeish does here:

Chief identified as Na-gun-ub (Minnesota Historical Society)
Aamoons and Naaganab don’t even look alike…

Naaganab (Minnesota Historical Society)
…but the Lac du Flambeau and Fond du Lac chiefs were probably photographed in St. Paul around the time they were both part of a delegation to President Lincoln in 1862.

Chippewa Delegation 1862 by Matthew Brady? (Minnesota Historical Society)
Naaganab (seated middle) and Aamoons (back row, second from left) are pretty easy to spot, and if you look closely, you’ll see Giishkitawag, Akiwenzii, and a younger Edawi-giizhig (4th, 5th, and 6th from left, back row) were there too. I can’t find individual photos of the other chiefs, but there is a place we can find their names.
Benjamin Armstrong, who interpreted for the delegation, included a version of the image in his memoir Early Life Among the Indians. He identifies the men who went with him as:
Ah-moose (Little Bee) from Lac Flambeau Reservation, Kish-ke-taw-ug (Cut Ear) from Bad River Reservation, Ba-quas (He Sews) from Lac Courte O’Rielles Reservation, Ah-do-ga-zik (Last Day) from Bad River Reservation, O-be-quot (Firm) from Fond du Lac Reservation, Sing-quak-onse (Little Pine) from La Pointe Reservation, Ja-ge-gwa-yo (Can’t Tell) from La Pointe Reservation, Na-gon-ab (He Sits Ahead) from Fond du Lac Reservation, and O-ma-shin-a-way (Messenger) from Bad River Reservation.
It appears that Armstrong listed the men according to their order in the photograph. He identifies Akiwenzii as “Ba-quas (He Sews),” which until I find otherwise, I’m going to assume the chief had two names (a common occurrence) since the village is the same. Aamoons, Giishkitawag, Edawi-giizhig and Naaganab are all in the photograph in the places corresponding to the order in Armstrong’s list. That means we can identify the other men in the photo.
I don’t know anything about O-be-quot from Fond du Lac (who appears to have been moved in the engraving) or S[h]ing-guak-onse from Red Cliff (who is cut out of the photo entirely) other than the fact that the latter shares a name with a famous 19th-century Sault Ste. Marie chief. Travis Armstrong’s outstanding website, chiefbuffalo.com, has more information on these chiefs and the mission of the delegation.
Seated to the right of Naaganab, in front of Edawi-giizhig is Omizhinawe, the brother of and speaker for Blackbird of Bad River. Finally, the broad-shouldered chief on the bottom left is “Ja-ge-gwa-yo (Can’t Tell)” from Red Cliff. This is Jajigwyong, the son of Chief Buffalo, who signed the treaties as a chief in his own right. Jayjigwyong, sometimes called Little Chief Buffalo, was known for being an early convert to Catholicism and for encouraging his followers to dress in European style. Indeed, we see him and the rest of the chiefs dressed in buttoned coats and bow-ties and wearing their Lincoln medals.
Wait a minute… button coats?… bow-ties?… medals?…. a chief identified as Buffalo…That reminds me of…
This image is generally identified as Chief Buffalo (Wikimedia Commons)
Anyway, with that mystery solved, we can move on to the next one. It concerns a photograph that is well-known to any student of Chequamegon-area history in the mid 19th century (or any Chequamegon History reader who looks at the banners on the side of this page).Noooooo!!!!!!! I’ve been trying to identify the person in The above “Chief Buffalo” photo for years, and the answer was in Armstrong all along! Now I need to revise this post among others. I had already begun to suspect it was Jayjigwyong rather than his father, but my evidence was circumstantial. This leaves me without a doubt. This picture of the younger Chief Buffalo, not his more-famous father.
The photo showing an annuity payment, must have been widely distributed in its day, because it has made it’s way into various formats in archives and historical societies around the world. It has also been reproduced in several secondary works including Ronald Satz’ Chippewa Treaty Rights, Patty Loew’s Indian Nations of Wisconsin, Hamilton Ross’ La Pointe: Village Outpost on Madeline Island, and in numerous other pamphlets, videos, and displays in the Chequamegon Region. However, few seem to agree on the basic facts:
When was it taken?
Where was it taken?
Who was the photographer?
Who are the people in the photograph?
We’ll start with a cropped version that seems to be the most popular in reproductions:

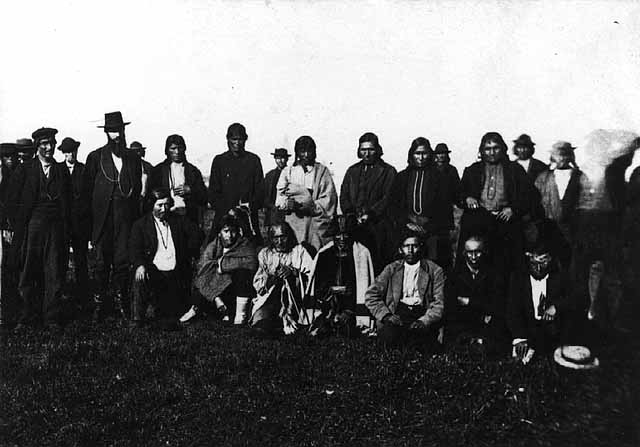
According to Hamilton Ross and the Wisconsin Historical Society: “Annuity Payment at La Pointe: Indians receiving payment. Seated on the right is John W. Bell. Others are, left to right, Asaph Whittlesey, Agent Henry C. Gilbert, and William S. Warren (son of Truman Warren).” 1870. Photographer Charles Zimmerman (more info).
In the next one, we see a wider version of the image turned into a souvenir card much like the ones of the chiefs further up the post:

According to the Minnesota Historical Society “Scene at Indian payment, Wisconsin; man in black hat, lower right, is identified as Richard Bardon, Superior, Wisconsin, then acting Indian school teacher and farmer” c.1871 by Charles Zimmerman (more info).
In this version, we can see more foreground and the backs of the two men sitting in front.

According to the Library of Congress: “Cherokee payments(?). Several men seated around table counting coins; large group of Native Americans stand in background.” Published 1870-1900 (more info).
The image also exists in engraved forms, both slightly modified…

According to Benjamin Armstrong: “Annuity papment [sic] at La Pointe 1852” (From Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians)
…and greatly-modified.

Harper’s Weekly August 5, 1871: “Payment of Indian Annuities–Coming up to the Pay Table.” (more info)
It should also be mentioned that another image exists that was clearly taken on the same day. We see many of the same faces in the crowd:
Scene at Indian payment, probably at Odanah, Wisconsin. c.1865 by Charles Zimmerman (more info)
We have a lot of conflicting information here. If we exclude the Library of Congress Cherokee reference, we can be pretty sure that this is an annuity payment at La Pointe or Odanah, which means it was to the Lake Superior Ojibwe. However, we have dates ranging from as early as 1852 up to 1900. These payments took place, interrupted from 1850-1852 by the Sandy Lake Removal, from 1837 to 1874.
Although he would have attended a number of these payments, Benjamin Armstrong’s date of 1852, is too early. A number of secondary sources have connected this photo to dates in the early 1850s, but outside of Armstrong, there is no evidence to support it.
Charles Zimmerman, who is credited as the photographer when someone is credited, became active in St. Paul in the late 1860s, which would point to the 1870-71 dates as more likely. However, if you scroll up the page and look at Giishkitaawag, Akiwenzii, and Aamoons again, you’ll see that these photos, (taken in the early 1860s) are credited to “Whitney & Zimmerman,” even though they predate Zimmerman’s career.
What happened was that Zimmerman partnered with Joel Whitney around 1870, eventually taking over the business, and inherited all Whitney’s negatives (and apparently those of James Martin as well). There must have been an increase in demand for images of Indian peoples in the 1870s, because Zimmerman re-released many of the earlier Whitney images.
So, we’re left with a question. Did Zimmerman take the photograph of the annuity payment around 1870, or did he simply reproduce a Whitney negative from a decade earlier?
I had a hard time finding any primary information that would point to an answer. However, the Summer 1990 edition of the Minnesota History magazine includes an article by Bonnie G. Wilson called Working the Light: Nineteenth Century Professional Photographers in Minnesota. In this article, we find the following:
“…Zimmerman was not a stay-at-home artist. He took some of his era’s finest landscape photos of Minnesota, specializing in stereographs of the Twin Cities area, but also traveling to Odanah, Wisconsin for an Indian annuity payment…”
In the footnotes, Wilson writes:
“The MHS has ten views in the Odanah series, which were used as a basis for engravings in Harper’s Weekly, Aug. 5, 1871. See also Winona Republican, Oct. 12, 1869 p.3;”
Not having access to the Winona Republican, I tried to see how many of the “Odanah series” I could track down. Zimmerman must have sold a lot of stereocards, because this task was surprisingly easy. Not all are labelled as being in Odanah, but the backgrounds are similar enough to suggest they were all taken in the same place. Click on them to view enlarged versions at various digital archives.

Scene at Indian Payment, Odanah Wisconsin (Minnesota Historical Society)

Chippewa Wedding (British Museum)

Domestic Life–Chippewa Indians (British Museum)

Chippewa Wedding (British Museum)
Finally…
So, if Zimmerman took the “Odanah series” in 1869, and the pay table image is part of it, then this is a picture of the 1869 payment. To be absolutely certain, we should try to identify the men in the image.
This task is easier than ever because the New York Public Library has uploaded a high-resolution scan of the Whitney & Zimmerman stereocard version to Wikimedia Commons. For the first time, we can really get a close look at the men and women in this photo.
They say a picture tells a thousand words. I’m thinking I could write ten-thousand and still not say as much as the faces in this picture.
To try to date the photo, I decided to concentrate the six most conspicuous men in the photo:
1) The chief in the fur cap whose face in the shadows.
2) The gray-haired man standing behind him.
3) The man sitting behind the table who is handing over a payment.
4) The man with the long beard, cigar, and top hat.
5) The man with the goatee looking down at the money sitting to the left of the top-hat guy (to the right in our view)
6) The man with glasses sitting at the table nearest the photographer
According to Hamilton Ross, #3 is Asaph Whittlesey, #4 is Agent Henry Gilbert, #5 is William S. Warren (son of Truman), and #6 is John W. Bell. While all four of those men could have been found at annuity payments as various points between 1850 and 1870, this appears to be a total guess by Ross. Three of the four men appear to be of at least partial Native descent and only one (Warren) of those identified by Ross was Ojibwe. Chronologically, it doesn’t add up either. Those four wouldn’t have been at the same table at the same time. Additionally, we can cross-reference two of them with other photos.

Asaph Whittlesey was an interesting looking dude, but he’s not in the Zimmerman photo (Wisconsin Historical Society).

Henry C. Gilbert was the Indian Agent during the Treaty of 1854 and oversaw the 1855 annuity payment, but he was dead by the time the “Zimmerman” photo was taken (Branch County Photographs)
Whittlesey and Gilbert are not in the photograph.
The man who I label as #5 is identified by Ross as William S. Warren. This seems like a reasonable guess, though considering the others, I don’t know that it’s based on any evidence. Warren, who shares a first name with his famous uncle William Whipple Warren, worked as a missionary in this area.
The man I label #6 is called John W. Bell by Ross and Richard Bardon by the Minnesota Historical Society. I highly doubt either of these. I haven’t found photos of either to confirm, but the Ireland-born Bardon and the Montreal-born Bell were both white men. Mr. 6 appears to be Native. I did briefly consider Bell as a suspect for #4, though.
Neither Ross nor the Minnesota Historical Society speculated on #1 or #2.
At this point, I cannot positively identify Mssrs. 1, 2, 3, 5, or 6. I have suspicions about each, but I am not skilled at matching faces, so these are wild guesses at this point:
#1 is too covered in shadows for a clear identification. However, the fact that he is wearing the traditional fur headwrap of an Ojibwe civil chief, along with a warrior’s feather, indicates that he is one of the traditional chiefs, probably from Bad River but possibly from Lac Courte Oreilles or Lac du Flambeau. I can’t see his face well enough to say whether or not he’s in one of the delegation photos from the top of the post.
#2 could be Edawi-giizhig (see above), but I can’t be certain.
#3 is also tricky. When I started to examine this photo, one of the faces I was looking for was that of Joseph Gurnoe of Red Cliff. You can see him in a picture toward the top of the post with the Roy brothers. Gurnoe was very active with the Indian Agency in Bayfield as a clerk, interpreter, and in other positions. Comparing the two photos I can’t say whether or not that’s him. Leave a comment if you think you know.
#5 could be a number of different people.
#6 I don’t have a solid guess on either. His apparent age, and the fact that the Minnesota Historical Society’s guess was a government farmer and schoolteacher, makes me wonder about Henry Blatchford. Blatchford took over the Odanah Mission and farm from Leonard Wheeler in the 1860s. This was after spending decades as Rev. Sherman Hall’s interpreter, and as a teacher and missionary in La Pointe and Odanah area. When this photo was taken, Blatchford had nearly four decades of experience as an interpreter for the Government. I don’t have any proof that it’s him, but he is someone who is easy to imagine having a place at the pay table.
Finally, I’ll backtrack to #4, whose clearly identifiable gray-streaked beard allows us to firmly date the photo. The man is Col. John H. Knight, who came to Bayfield as Indian Agent in 1869.

Col. John H. Knight (Wisconsin Historical Society)
Knight oversaw a couple of annuity payments, but considering the other evidence, I’m confident that the popular image that decorates the sides of the Chequamegon History site was indeed taken at Odanah by Charles Zimmerman at the 1869 annuity payment.
Do you agree? Do you disagree? Have you spotted anything in any of these photos that begs for more investigation? Leave a comment.
As for myself, it’s a relief to finally get all these photo mysteries out of my post backlog. The 1870 date on the Zimmerman photo reminds me that I’m spending too much time in the later 19th century. After all, the subtitle of this website says it’s history before 1860. I think it might be time to go back for a while to the days of the old North West Company or maybe even to Pontiac. Stay tuned, and thanks for reading,
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: Conclusion
December 7, 2013
This post concludes the Chief Buffalo Picture Search, a series of posts attempting to determine which images of Chief Buffalo are of the La Pointe Ojibwe leader who died in 1855, and which are of other chiefs named Buffalo. To read from the beginning, click here to read Chief Buffalo Picture Search: Introduction.
 This is Chief Buffalo from St. Croix, not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe.
This is Chief Buffalo from St. Croix, not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe.
This lithograph from McKenney and Hall’s History of the Indian Tribes, was derived from an original oil painting (now destroyed) painted in 1824 by Charles Bird King.Buffalo from St. Croix was in Washington in 1824. Buffalo from La Pointe was not. Read:
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The King and Lewis Lithographs

This could be Chief Buffalo from La Pointe. It could also be Chief Buffalo from St. Croix
This lithograph from James Otto Lewis’ The Aboriginal Port-Folio is based on a painting done by Lewis at the Treaty of Prairie du Chien in 1825 or at the Treaty of Fond du Lac in 1826 (Lewis is inconsistent in his own identification). The La Pointe and St. Croix chiefs were at both treaties. Read:
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The King and Lewis Lithographs

This is not Chief Buffalo of La Pointe. This is the clan marker of Oshkaabewis, a contemporary chief from the headwaters of the Wisconsin River.
The primary sources clearly indicate that this birch bark petition was carried by Oshkaabewis to Washington in 1849 as part of a delegation of Lake Superior Ojibwe protesting Government removal plans. Read:

One of these men could be Chief Buffalo of La Pointe.
This engraving from Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians appears to depict the 1852 Washington Delegation led by Buffalo. However, the men aren’t identified individually, and the original photograph hasn’t surfaced. Read:
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Armstrong Engraving

 This is not Chief Buffalo of La Pointe. This is Buffalo the war chief from Leech Lake.
This is not Chief Buffalo of La Pointe. This is Buffalo the war chief from Leech Lake.
Buffalo and Flatmouth, two Pillager (Leech Lake) leaders had their faces carved in marble in Washington in 1855. Buffalo was later copied in bronze, and both busts remain in the United States capitol. The chiefs were part of a Minnesota Ojibwe delegation making a treaty for reservations in Minnesota. Buffalo of Leech Lake was later photographed in St. Paul. Read:
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Capitol Busts
 This could be Chief Buffalo of La Pointe.
This could be Chief Buffalo of La Pointe.
Very little is known about the origin of this image. It is most likely Chief Buffalo’s son Jayjigwyong, who was sometimes called “The Little Buffalo.” Read:
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Island Museum Painting
As it currently stands, out of the seven images investigated in this study, four are definitely not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe, and the other three require further investigation. The lithograph of Pee-che-kir from McKenney and Hallʼs History of the Indian Tribes, based on the original painting by Charles Bird King, is Buffalo from St. Croix. The marble and bronze busts in Washington D.C., as well as the carte-d-visite from Whitneyʼs in St. Paul, show Bizhiki the war chief from Leech Lake. The pictograph of the crane, once identified with Buffalo, is actually the Crane-clan chief Oshkaabewis. There is not enough information yet to make a determination on the lithograph of Pe-schick-ee from James Otto Lewisʻ Aboriginal Port Folio, on the image of the 1852 delegation in Armstrongʼs Early Life Among the Indians, or on the photo and painting of the man in the military coat.
In the end, the confusion about all of these images can be attributed to authors with motivations other than recording an accurate history of these men, authors who were not familiar enough with this time period to realize that there was more than one Buffalo. Charles Bird King and Francis Vincenti created some beautiful work in the national capital, but their ultimate goal was to make a record of the look of a supposedly vanishing people. The Pillager Bizhiki was chosen to sit for the sculpture not for who he was, but for what he looked like. The St. Croix Buffalo was chosen because he happened to be in Washington when King was painting. Over a century later, scholars like Horan and Holzhueter being more concerned with the art itself than the people depicted, furthered the confusion. Unfortunately, these mistakes had consequences for the study of history.
While this new information, especially in regard to the busts in Washington, may be discouraging to the people of Red Cliff and other descendants of Buffalo from La Pointe, there is also cause for excitement. The study of these images opens up new lines of inquiry into the last three decades of the chief’s life, a pivotal time in Ojibwe history. Inaccuracies about his life can be corrected, and people will stop having to come up with stories to connect Buffalo to images that were never him to begin with.
My hope is that this investigation will encourage people to learn more about all three Chief Buffalos, all of whom represented their people in Washington, as well as the other Ojibwe leaders from this time period. It is this hopeful story, as well as the possibility of further investigation into the three remaining images, that should lead Chief Buffaloʼs descendants to feel optimism rather than disappointment.
For now, this concludes the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search. I will update in the future, however, if new evidence surface. Thanks for reading, and feel free to add your thoughts in the comments.
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Island Museum Painting
November 9, 2013
This post is one of several that seek to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, please read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.

(Wisconsin Historical Society, Image ID: 3957)
If any image has been as closely tied to Chief Buffalo from La Pointe as the the bust of the Leech Lake Buffalo in Washington, it is an image of a kindly but powerful-looking man in a U.S. Army jacket with a medal around his neck. This image appears on the cover of the 1999 edition of Walleye Warriors, by treaty-rights activist Walter Bresette and Rick Whaley. It is identified as Buffalo in both Ronald Satzʼs Chippewa Treaty Rights, and Patty Loewʼs Indian Nations of Wisconsin. It occupies a prominent position in the collections of the Wisconsin Historical Society and hangs in the Madeline Island Museum, but in spite of the enduring popularity of this image, very little is known about it.
As I have not been able to thoroughly examine the originals or find any information whatsoever about their creation, chain of custody, or even when they entered the Historical Society’s collections, this post will be the most speculative of the Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
There are two versions of this image. One appears to be an early type of photograph. The Wisconsin Historical Society describes it as “over-painted enlargement, possibly from a double-portrait (possibly an ambrotype).” I’ve been told by staff that the painting that hangs in the museum is a copy of this earlier version.
A photograph of the original image is in the Societyʼs archives as part of the Hamilton Nelson Ross collection. On the back of the photo, “Chief Buffalo, Grandson of Great Chief Buffalo” is handwritten, presumably by Ross. This description would seem to indicate that the image shows one of Chief Buffaloʼs grandsons. However, we need to be careful trusting Ross as a source of information about Buffalo’s family.
Ross, a resident of Madeline Island, gathered volumes of information on his home community in preparation for his book La Pointe Village Outpost on Madeline Island (1960). Although the book is exhaustively researched and highly detailed about the white and mix-blooded populations of the Island, it contains precious little information about individual Indians. The image of Buffalo is not in the book. In fact, the only mention of the chief comes in a footnote about his grave on page 177:
O-Shaka was also known as O-Shoga and Little Buffalo, and he was the son of Chief Great Buffalo. The latter’s Ojibway name was Bezhike, but he was also known as Kechewaishkeenh–the latter with a variety of spellings. Bezhike’s tombstone, in the Indian cemetery, has had the name broken off…
Oshogay was not Buffalo’s son (though he may have been a son-in-law), and he was not the man known as “Little Buffalo,” but until his untimely death in 1853, he seemed destined to take over leadership of Buffalo’s “Red Cliff” faction of the La Pointe Band. The one who did ultimately step into that role, however, was Buffalo’s son Jayjigwyong (Che-chi-gway-on):

Drew, C.K. Report of the Chippewa Agency of Lake Superior. 26 Oct. 1858. Printed in Report of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs. 1858 (Digitized by Google Books)
We will return to Jayjigwyong later in the post, but for now, let’s examine the image itself.
The man in the picture wears an early 19th-century army jacket and a medal. This is consistent with the practices of Chief Buffalo’s day. The custom of handing out flags, jackets, and medals goes back at least to the 1700s with the French. The practice continued under the British and Americans as a way of recognizing certain individuals as chiefs and asserting imperial claims. For the chiefs, the items were symbolic of agreements and alliances. Large councils, treaty signings, and diplomatic missions were all occasions where they were given out. Buffalo had received medals and jackets from the British, and between 1820 and 1855, he took part in the negotiations of at least five treaties, many council meetings and annuity payments, visited Washington, and frequently went back and forth to the agency at Sault Ste. Marie. The United States Government favored Buffalo over the more forcefully-independent chiefs on the Ojibwe-Dakota frontier in Minnesota. Considering all this, it is likely that Buffalo received many jackets, flags, and medals from the Americans over the course of his long interaction with them. An excerpt from a letter by teacher Granville Sproat, who lived in the Lake Superior region in the 1830s reads:
Ke-che Be-zhe-kee, or Big Buffalo, as he was called by the Americans, was then chief of that band of Ogibway Indians who dwell on the south-west shores of Lake Superior, and were best known as the Lake Indians. He was wise and sagacious in council, a great orator, and was much reverenced by the Indians for his supposed intercourse with the Man-i-toes, or spirits, from whom they believed he derived much of his eloquence and wisdom in governing the affairs of the tribe.
“In the summer of 1836, his only son, a young man of rare promise, suddenly sickened and died. The old chief was almost inconsolable for his loss, and, as a token of his affection for his son, had him dressed and laid in the grave in the same military coat, together with the sword and epaulettes, which he had received a few months before as a present from the great father [president] at Washington. He also had placed beside him his favorite dog, to be his companion on his journey to the land of souls (qtd. in Peebles 107).
It is strange that Sproat says Buffalo had only one son given that his wife Florantha Sproat references another son in her description of this same funeral, but sorting out Buffalo’s descendants has never been an easy task. There are references to many sons, daughters, and wives over the course of his very long life.
Another description from the Treaty of 1842 reads:
On October 1 Buffalo appeared, wearing epaulettes on his shoulders, a hat trimmed with tinsel, and a string of bear claws about his neck (Dietrich qtd. in Paap 177-78).
From these accounts we know that Buffalo had these kinds of coats, but dozens of other Ojibwe chiefs would have had similar ones, so the identification cannot be made based on the existence of the coat alone. Consider Naaganab at the 1855 annuity payment:
Na-gon-ub is head chief of the Fond du Lac bands; about the age of forty, short and close built, inclines to ape the dandy in dress, is very polite, neat and tidy in his attire. At first, he appeared in his native blanket, leggings, &c. He soon drew from the Agent a suit of rich blue broadcloth, fine vest, and neat blue cap,–his tiny feet in elegant finely-wrought moccasins. Mr. L., husband of Grace G., with whom he was a special favorite, presented him with a pair of white kid gloves, which graced his hands on all occasions. Some two or three years since, he visited Washington, a delegate from his tribe. Upon this journey, some one presented him with a pair of large and gaudy epaulettes, said to be worth sixty dollars. These adorned his shoulders daily; his hair was cut shorter than their custom. He quite inclined to be with, and to mingle in the society, of the officers, and of white men. These relied on him more, perhaps, than any other chief, for assistance among the Chippewas… (Morse pg. 346)

Portrait of Naw-Gaw-Nab (The Foremost Sitter) n.d by J.E. Whitney of St. Paul (Smithsonian)
In many ways, this description of Naaganab fits the image better than any description of Buffalo I’ve seen. The man is dressed in European fashion, has short hair, and large epaulets. We also know that Naaganab had presidential medals, since he continued to display them until his death in the 1890s. The image isn’t dated, but if it truly is an ambrotype, as described by the State Historical Society, that is a technique of photography used mostly in the late 1850s and 1860s. When Buffalo died in 1855, he was reported to be in his nineties. Naaganab would have been in his forties or fifties at that time. To me, the man in the image appears middle-aged rather than elderly.
So is Naaganab the man in the picture? I don’t think so. For one, there are multiple photographs of the Fond du Lac chief out there. The clothing and hairstyle largely match, but the face is different. The other thing to consider is that this image, to my knowledge, has never been identified with Naaganab. Everything I’ve ever seen associates it with the name Buffalo.
However, there is a La Pointe chief who was a political ally of Naaganab, also dressed in white fashion, could have easily owned a medal and fancy army jacket, would have been middle-aged in the 1850s, and bore the English name of “Buffalo.” It was Jayjigwyong, the son of Chief Buffalo.
Alfred Brunson recorded the following in 1843:

(pg. 158) From elsewhere in the account, we know that the “fifty” year-old is Chief Buffalo. This is odd, as most sources had Buffalo in his eighties at that time.

(pg. 191)
Unlike his famous father, Jayjigwyong, often recorded as “Little Buffalo,” is hardly remembered, but he is a significant figure in the history of our region. He was a signatory of the treaties of 1837, 1847, and 1854. He led the faction of the La Pointe Band that felt that rapid assimilation represented the best chance for the Ojibwe to survive and keep their lands. In addition to wearing white clothing and living in houses, Jayjigwyong was Catholic and associated more with the mix-blooded population of the Island than with the majority of the La Pointe band who sought to maintain their traditions at Bad River.
According to James Blackbird, whose father Makadebineshiinh (Black Bird) led the Bad River faction, it was Jayjigwyong who chose where the Red Cliff reservation was to be. James Blackbird, about eleven or twelve at the time of the Treaty of 1854, would have known both the elder and younger Buffalo.

Statement of James Blackbird in the Matters of the Allotments on the Bad River Reservation, Wis. Odanah, 23 Sep. 1909. Published in Condition of Indian affairs in Wisconsin: hearings before the Committee on Indian Affairs, United States Senate, [61st congress, 2d session], on Senate resolution, Issue 263. United States Congress. 1910. Pg. 202.
The younger Blackbird, offered more information about the younger Buffalo in another publication.
Even though it is from 1915, there are a number of items in this account that if accurate are very relevant to pre-1860 history. For this post, I’ll stick to the two that involve Jayjigwyong. This is the only source I’ve ever seen that refers to Chief Buffalo marrying a white woman captured on a raid. This lends further credence to the argument explored by Dietrich and Paap that Chief Buffalo fought in the Ohio Valley wars of the 1790s. It also begs the question of whether being perceived as a “half-breed” had an impact on Jayjigwyong’s decisions as an adult.

James Blackbird (seated) with interpreter John Medeguan in Washington, 1899. (Photo by Gil DeLancy, Smitsonian Collections)
The other interesting part of the statement is that James Blackbird says his father was pipe carrier for Jayjigwyong. This would be surprising as Blackbird was the most influential La Pointe chief after the death of Buffalo. However, this idea of Jayjigwyong, inheriting the symbolic “head chief” title from his father can also be seen in the following document from 1857:

Published in Annual Report of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs to the Secretary of the Interior. Office of Indian Affairs. 1882. pg. 299. (Digitized by Google Books)
Today the fishing ground at the tip of Madeline Island is now considered part of the Bad River Reservation, but it was the Red Cliff chief who picked it out. This shows how the political division of the La Pointe Band into two distinct entities took several years to take shape, and was not an abrupt split at the Treaty of 1854.
Jayjigwyong continued to be regarded as a chief until his death in 1860:

Drew, C.K. Report on the Chippewas of Lake Superior. Red Cliff Agency. 29 Oct. 1860. Pg. 51 of Annual Report of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs. Bureau of Indian Affairs. 1860. (Digitized by Google Books). Zhingob (Shing-oop) was Naaganab’s cousin and the hereditary chief at Fond du Lac. Also known as Nindibens, he figures prominently in Edmund F. Ely’s journals of the mid-1830s.
Future generations of the Buffalo family continued to be looked at as hereditary chiefs in Red Cliff, and sources can be found calling these grandsons and great-grandsons “Chief Buffalo.”

J.H. Beers and Co. Commemorative Biographical Record of the Upper Lake Region. 1905. Pg. 379. (Digitized by Google Books).
Antoine brings us full circle. If we remember, Hamiton Ross wrote that the image of the chief in the army jacket was Chief Buffalo’s grandson. And while we don’t know where Ross got his information, and he made mistakes about Buffalo’s family elsewhere, we have to consider that Antoine Buffalo was an adult by 1852 and he could have inherited his father’s, or grandfather’s, medal and coat.
The Verdict
Although we’ve uncovered several lines of inquiry for this image, all the evidence is circumstantial. Until we know more about the creation and chain of custody, it’s impossible to rule Chief Buffalo in or out. My gut tells me it’s Buffalo’s son, Jajigwyong, but it could be his grandson, Naaganab, or and entirely different chief. We don’t know.
Sources:
Brunson, Alfred. A Western Pioneer, Or, Incidents of the Life and times of Rev. Alfred Brunson Embracing a Period of over Seventy Years. Cinncinnati: Hitchchock and Walden, 1872. Print.
Commemorative Biographical Record of the Upper Lake Region. Chicago: J. H. Beers &, 1905. Print.
Ely, Edmund Franklin, and Theresa M. Schenck. The Ojibwe Journals of Edmund F. Ely, 1833-1849. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2012. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Peebles, J. M. Immortality, and Our Employments Hereafter. With What a Hundred Spirits, Good and Evil, Say of Their Dwelling Places. Boston: Colby and Rich, 1880. Print.
Ross, Hamilton Nelson. La Pointe, Village Outpost. St. Paul: North Central Pub., 1960. Print
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. The Voice of the Crane Echoes Afar: The Sociopolitical Organization of the Lake Superior Ojibwa, 1640-1855. New York: Garland Pub.,1997. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Whaley, Rick, and Walter Bresette. Walleye Warriors: The Chippewa Treaty Rights Story. Warner, NH: Tongues of Green Fire, Writers Pub. Cooperative, 1999. Print.
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Armstrong Engraving
October 3, 2013
This post is one of several that seek to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, please read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
In 1892, thirty-seven years after the death of the La Pointe Chief Buffalo, a curious book appeared on the market. It was printed by A.W, Bowron of Ashland, Wisconsin, just south of Madeline Island at the end of Chequamegon Bay. It was titled Early Life Among the Indians: Reminiscences From the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong. More than any other book, this work has informed the public about the life of Buffalo, and it contains the only complete account of his famous 1852 journey to Washington D.C.
Benjamin Armstrong was born in Alabama. As a young man, he travelled throughout the South and up the Mississippi River eventually making it to Wisconsin. He learned Ojibwe, settled on Madeline Island, and married one of Buffalo’s nieces. Over time, he became Buffalo’s personal interpreter and accompanied him to Washington. His work translating the 1854 Treaty of La Pointe, which established reservations in Wisconsin on largely favorable terms to the Ojibwe, led Buffalo to refer to him as an adopted son. The chief even inserted a provision for a section of land for Armstrong within the ceded territory. The land Armstrong chose was at the site where downtown Duluth would rise.
Over the next several decades, Armstrong battled poverty, temporary blindness, and alcohol. He was duped into trading away his claim on Duluth and lost his bid to regain it in the U.S. Supreme Court. Had he hung on to the land, it would have made him very wealthy, but instead, he remained poor in the Chequamegon region. As he neared the end of his life, he decided to team with Thomas P. Wentworth of Ashland to record his memoirs. The work was completed in 1891 and went to press the following year.
Early Life Among the Indians is a complex work. Much of it contains rich details that could only have come from the true experiences of an insider. Other parts appear to be wholly fabricated. Armstrong’s tone is more that of a northwoods storyteller than it is of a academic historian. Faced with this dilemma, modern scholars of Ojibwe history have either fully embraced Armstrong or have completely rejected him. For the purposes of this study, we cannot do either.

Some of the images in Armstrong’s memior seem to have been created especially for the work and were not derived from earlier photographs (Marr and Richards Co.).
In the first two chapters, Armstrong describes the trip to Washington. He mentions himself, Buffalo, and the young orator Oshogay, making the trip along with four other Ojibwe men. From other sources, we know that a young mixed-blood from La Pointe, Vincent Roy Jr., was also part of the delegation. Within these two chapters, there are two images. Each may contain a representation of Buffalo.
All of the images in the book are from engravings produced by the Marr and Richards Engraving Company of Milwaukee. Born and trained in Germany, master engraver John Marr had started the company with the American-born George Richards in 1888. Their highly-precise maps, and illustrations appeared throughout the upper Midwest during this time period. For Early Life Among the Indians, it appears that Marr and Richards produced two types of engravings. One type was derived from original photographs, and the others were original designs to illustrate incidents from Armstrong’s stories. Of the latter type, a plate between pages 32 and 33 shows an image of five Indians huddled around a fire during a fierce thunderstorm. A bearded figure in a raincoat, presumably Armstrong, stands in the background.
This image, called Encountered on the Tpip [sic] to Washington., illustrates a part of Armstrong’s story where the delegation had to pull their canoe out of the water during a storm on the south shore of Lake Superior on the first leg of the journey. Of the five Ojibwe men shown, the one with the most feathers, nearest the viewer with his back and profile visible is the most prominent. However, all five are simple renderings that play into Indian stereotypes of the day and do not appear to be based on any real images. So, while the illustrators may have intended one to show Buffalo, this image was produced long after his death and does nothing to suggest what he would have looked like.

Washington Delegation, June 22, 1852: Chief Buffalo led this famous Ojibwe delegation to Washington, so it is assumed he is one of the men in this engraving, but which one? The original photograph has not been located (Marr and Richards Co.).
The image labelled Washington Delegation, June 22,1852, between pages 16 and 17, is much more intriguing. It shows three seated men in front of three standing men. The man standing on the right appears to be Armstrong, but the rest of them are not identified. There has been a lot of speculation whether or not this image shows Chief Buffalo. The man seated in the middle with the large white sash across his chest was featured on on poster of Buffalo released by the Minnesota Historical Society in the 1980s. He does appear to be the oldest and most prominent of the group. However, the man holding a pipe sitting to his left (bottom right in the picture)was used as the model for the large outdoor mural of Buffalo on the corner of Highways 2 and 13 in Ashland.
Besides the title and the engraver’s mark, there is no other information to identify the origin of this image. It almost certainly came from a photograph. Two similar engravings, found elsewhere in the book can be traced to specific photos. One Armstrong identifies as being the 1862 Ojibwe delegation to President Lincoln. In the engraving, seven chiefs stand behind three who sit. Again, the men are not identified, but Armstrong lists the names of the chiefs who accompanied him on pages 66 and 67. The Fond du Lac chief, Naaganab (Sits in Front) is identifiable from other photographs. As his name would suggest, he is seated in front in the center.
The photograph this engraving was made from was taken by the famous Civil War photographer Matthew Brady, and it can be found in the collections of the Minnesota Historical Society. From the postures and facial expressions of the men, it is clear the engraving was made from this photo. However, the two images are not exact duplicates. The man standing third from the left in the photo appears to have been moved to the far right in the engraving, and to the right of him, we see another man who is not in the photo. Because the photograph from MHS cuts off immediately to the right of the man who is third from the right in the engraving, it is impossible to know whether or not anyone stood there when the photo was taken.
The other engraving based on a photograph appears between pages 134 and 135. Armstrong identifies it as Annuity papement [sic] at La Pointe, 1852. The photograph it comes from, by Charles Zimmerman, is well known to scholars of this time period, and it appears in many secondary works. One copy is held by the Wisconsin Historical Society. It shows four government officials from La Pointe seated at a table surrounded by Ojibwe men and women waiting to receive their treaty payments. Sources vary on the date. The Historical Society identifies it as 1870 and describes it as “Indians receiving payment. Seated on the right is John W. Bell. Others are, left to right, Asaph Whittlesey, Agent Henry C. Gilbert, and William S. Warren (son of Truman Warren).”
While the engraving of the 1852 Delegation is clearly also from a photograph, the original has not been located. If it exists, and contains any more identifying information, it represents possibly the best opportunity to see what Buffalo looked like. We need to find the photo!
The Verdict
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Ashland Chamber of Commerce. “Ashland Mural Walk.” Ashland Wisconsin. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 June 2012. <http://www.visitashland.com/>.
Brady, Matthew. Ojibwe Men (Possibly at 1857 or 1862 Treaty Signing at Washington D.C.). c.1862. Photograph. Minnesota Historical Society, Washington. MHS Visual Resource Database. Minnesota Historical Society, 2012. Web. 28 June2012. <http://collections.mnhs.org/visualresources/>.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
Merrill, Peter C. German Immigrant Artists in America: A Biographical Dictionary. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow, 1997. Print.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s
Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of
Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Zimmerman, Charles A. Annuity Payment at La Pointe. c.1852-1870. Photograph. Wisconsin Historical Society, La Pointe, WI. Wisconsin Historical Images. Wisconsin Historical Society, 1996-2012. Web. 28 June 2012. <http://http://www.wisconsinhistory.org/whi>.
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: The Capitol Busts
July 17, 2013
This post is one of several that seek to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, please read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
Posts on Chequamegon History are generally of the obscure variety and are probably only interesting to a handful of people. I anticipate this one could cause some controversy as it concerns an object that holds a lot of importance to many people who live in our area. All I can say about that is that this post represents my research into original historical documents. I did not set out to prove anybody right or wrong, and I don’t think this has to be the last word on the subject. This post is simply my reasoned conclusions based on the evidence I’ve seen. Take from it what you will.

Be sheekee, or Buffalo by Francis Vincenti, Marble, Modeled 1855, Carved 1856 (United States Senate)

Be Sheekee: A Chippewa Warrior from the Sources of the Mississippi, bronze, by Joseph Lassalle after Francis Vincenti, House wing of the United States Capitol (U.S. Capitol Historical Society).
“A Chippewa Warrior from the Sources of the Mississippi”
There is no image that has been more widely identified with Chief Buffalo from La Pointe than the marble bust and bronze copy in the U.S. Capitol Building in Washington D.C. Red Cliff leaders make a point of visiting the statues on trips to the capital city, the tribe uses the image in advertising and educational materials, and literature from the United States Senate about the bust includes a short biography of the La Pointe chief.
I can trace the connection between the bust and the La Pointe chief to 1973, when John O. Holzhueter, editor of the Wisconsin Magazine of History wrote an article for the magazine titled Chief Buffalo and Other Wisconsin-Related Art in the National Capitol. From Holzhueterʼs notes we can tell that in 1973, the rediscovery of the story of the La Pointe Buffalo was just beginning at the Wisconsin Historical Society (the publisher of the magazine). Holzhueter deserves credit for helping to rekindle interest in the chief. However, he made a critical error.
In the article he briefly discusses Eshkibagikoonzhe (Flat Mouth), the chief of the Leech Lake or Pillager Ojibwe from northern Minnesota. Roughly the same age as Buffalo, Flat Mouth is as prominent a chief in the history of the upper Mississippi as Buffalo is for the Lake Superior bands. Had Holzhueter investigated further into the life of Flat Mouth, he may have discovered that at the time the bust was carved, the Pillagers had another leader who had risen to prominence, a war chief named Buffalo.
Holzhueter clearly was not aware that there was more than one Buffalo, and thus, he had to invent facts to make the history fit the art. According to the article (and a book published by Holzhueter the next year) the La Pointe Buffalo visited President Pierce in Washington in January of 1855. Buffalo did visit Washington in 1852 in the aftermath of the Sandy Lake Tragedy, but the old chief was nowhere near Washington in 1855. In fact, he was at home on the island in declining health having secured reservations for his people in Wisconsin the previous summer. He would die in September of 1855. The Buffalo who met with Pierce, of course, was the war chief from Leech Lake.
“He wore in his headdress 5 war-eagle feathers“
The Pillager Buffalo was in Washington for treaty negotiations that would transfer most of the remaining Ojibwe land in northern Minnesota to the United States and create reservations at the principal villages. The minutes of the February 1855 negotiations between the Minnesota chiefs and Indian Commissioner George Manypenny are filled with Ojibwe frustration at Manypennyʼs condescending tone. The chiefs, included the powerful young Hole-in-the-Day, the respected elder Flat Mouth, and Buffalo, who was growing in experience and age, though he was still considerably younger than Flat Mouth or the La Pointe Buffalo. The men were used to being called “red children” in communications with their “fathers” in the government, but Manypennyʼs paternalism brought it to a new low. Buffalo used his clothing to communicate to the commissioner that his message of assimilation to white ways was not something that all Ojibwes desired. Manypennyʼs words and Buffaloʼs responses as interpreted by the mix- blooded trader Paul Beaulieu follow:
The commissioner remarked to Buffalo, that if he was a young man he would insist upon his dispensing with his headdress of feathers, but that, as he was old, he would not disturb a custom which habit had endeared to him.
Buffalo repoled ithat the feathered plume among the Chippewas was a badge of honor. Those who were successful in fighting with or conquering their enemies were entitled to wear plumes as marks of distinction, and as the reward of meritorious actions.The commissioner asked him how old he was.
Buffalo said that was a question which he could not answer exactly. If he guessed right, however, he supposed he was about fifty. (He looked, and was doubtless, much
older).Commissioner. I would think, my firend, you were older than that. I would like to philosophise with you about that headdress, and desired to know if he had a farm, a house, stock, and other comforts about him.
Buffalo. I have none of those things which you have mentioned. I live like other members of the tribe.
Commissioner. How long have you been in the habit of painting—thirty years or more?
Buffalo. I can not tell the number of years. It may have been more or it may have been less. I have distinguished myself in war as well as in peace among my people and the whites, and am entitled to the distinction which the practice implies.
Commissioner. While you, my firend, have been spending your time and money in painting your face, how many of your white brothers have started without a dollar in the world and acquired all those things mentioned so necessary to your comfort and independent support. The paint, with the exception of what is now on my friend’s face, has disappeared, but the white persons to whom I alluded by way of contrast are surrounded by all the comforts of life, the legitimate fruits of their well-directed industry. This illustrates the difference between civilized and savage life, and the importance of our red brothers changing their habits and pursuits for those of the white.

Major General Montgomery C. Meigs was a Captain before the Civil War and was in charge of the Capitol restoration, As with Thomas McKenney in the 1820s, Meigs was hoping to capture the look of the “vanishing Indian.” He commissioned the busts of the Leech Lake chiefs during the 1855 Treaty negotiations. (Wikimedia Images)
While Manypenny clearly did not like the Ojibwe way of life or Buffaloʼs style of dress, it did catch the attention of the authorities in charge of building an extension on the U.S. Capitol. Captain Montgomery Meigs, the supervisor, had hired numerous artists and much like Thomas McKenney two decades earlier, was looking for examples of the indigenous cultures that were assumed to be vanishing. On February 17th, Meigs received word from Seth Eastman that the Ojibwe delegation was in town.
The Captain met Bizhiki and described him in his journal:
“He is a fine-looking Indian, with character strongly marked. He wore in his headdress 5 war-eagle feathers, the sign of that many enemies put to death by his hand, and sat up, an old murderer, as proud of his feathers as a Frenchman of his Cross of the Legion of Honor. He is a leading warrior rather than a chief, but he has a good head, one which would not lead one, if he were in the Senate, to think he was not fit to be the companion of the wise of the land.”
Buffalo was paid $5.00 and sat for three days with the skilled Italian sculptor Francis Vincenti. Meigs recorded:
“Vincenti is making a good likeness of a fine bust of Buffalo. I think I will have it put into marble and placed in a proper situation in the Capitol as a record of the Indian culture. 500 years hence it will be interesting.”
Vincenti first formed clay models of both Buffalo and Flat Mouth. The marbles would not be finished until the next year. A bronze replica of Buffalo was finished by Joseph Lassalle in 1859. The marble was put into the Senate wing of the Capitol, and the bronze was placed in the House wing.
Clues in the Marble
The sculptures themselves hold further clues that the man depicted is not the La Pointe Buffalo. Multiple records describe the La Pointe chief as a very large man. In his obituary, recorded the same year the statue was modeled, Morse writes:
Any one would recognize in the person of the Buffalo chief, a man of superiority. About the middle height, a face remarkably grave and dignified, indicating great thoughtfulness; neat in his native attire; short neck, very large head, and the most capacious chest of any human subject we ever saw.
At the time of his death, he was thought to have been over ninety years old. The man in the sculpture is lean and not ninety. In addition, there is another clue that got by Holzhueter even though he printed it in his article. There is a medallion around the neck of the bronze bust that reads, “Beeshekee, the BUFFALO; A Chippewa Warrior from the Sources of the Mississippi…” This description works for a war chief from Leech Lake, but makes no sense for a civil chief and orator from La Pointe.
Another Image of the Leech Lake Bizhiki

Be-She-Kee (Buffalo), Head Chief of the Leech Lake Chippewas c. 1863 (Whitney’s Gallery, St. Paul)
The Treaty of 1855 was signed on February 22, and the Leech Lake chiefs returned to Minnesota. By the outbreak of the Civil War, Flat Mouth had died leaving Buffalo as the most prominent Pillager chief. Indian-White relations in Minnesota grew violent in 1862 as the U.S.- Dakota War (also called the Sioux Uprising) broke out in the southern part of the state. The Gull Lake chief, Hole in the Day, who had claimed the title of head of the Ojibwes, was making noise about an Ojibwe uprising as well. When he tried to use the Pillagers in his plan, Buffalo voiced skepticism and Hole in the Dayʼs plans petered out. In 1863, Buffalo returned to Washington for a new treaty. Ironically, he was still very much alive in the midst of complicated politics in a city where his bust was on display as monument to the vanishing race.
At some point during these years, the Pillager Buffalo had his photograph taken by Whitneyʼs Gallery in St. Paul. Although the La Pointe Buffalo was dead by this time, internet sites will occasional connect it with him even with an original caption that reads “Head Chief of the Leech Lake Chippewas.”
The Verdict
Although it wasn’t the outcome I was hoping for, my research leads me to definitively conclude that the busts in the U.S. Capitol are of Buffalo the Leech Lake war chief. It’s disappointing for our area to lose this Washington connection, but our loss it Leech Lake’s gain. Though less well-known than the La Pointe band’s chief, their chief Buffalo should also be remembered for his role in history.

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe: This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe: This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe: This is Chief Buffalo from Leech Lake.
Sources:
Holzhueter, John O. “Chief Buffalo and Other Wisconsin-Related Art in the National Capitol.” Wisconsin Magazine of History 56.4 (1973): 284-89. Print.
———– Madeline Island & the Chequamegon Region. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1974. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Kloss, William, Diane K. Skvarla, and Jane R. McGoldrick. United States Senate Catalogue of Fine Art. Washington, D.C.: U.S. G.P.O., 2002. Print.
Legendary Waters Resort and Casino. Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa, 2012. Web. 28 June 2012. <http://www.legendarywaters.com/>.
Minutes of the 1855 Treaty. 1855. MS. Bureau of Indian Affairs, Washington. Gibagdinamaagoom. White Earth Tribal and Community College Et. Al. Web. 28 June 2012. <gibagadinamaagoom.info/images/1855TreatyMinutes.pdf>.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Treuer, Anton. The Assassination of Hole in the Day. St. Paul, MN: Borealis, 2010. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Whitney’s Gallery. Be-she-kee (Buffalo). c.1860. Photograph. Minnesota Historical Society, St. Paul. MHS Visual Resource Database. Minnesota Historical Society, 2012. Web. 28 June 2012. <http://collections.mnhs.org/visualresources/>.
Wolff, Wendy, ed. Capitol Builder: The Shorthand Journals of Montgomery C. Meigs, 1853-1859, 1861. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC: 2001. Print.
This post is on of several that seeks to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
Today’s post looks at two paintings from the 1820s of Ojibwe men named Bizhiki (Buffalo). The originals are lost forever, but the images still exist in the lithographs that follow.

Pee-che-kir: A Chippewa Chief Lithograph from McKenney and Hall’s History of the Indian Tribes of North America based on destroyed original by Charles Bird King; 1824. (Wikimedia Images)

Pe-shick-ee: A Celebrated Chippeway Chief from the Aboriginal Port-Folio by James Otto Lewis. The original painting was done by Lewis at Prairie du Chien or Fond du Lac of Lake Superior in 1825 or 1826 (Wisconsin Historical Society).
1824 Delegation to Washington
Chronologically, the first known image to show an Ojibwe chief named Buffalo appeared in the mid-1820s at time when the Ojibwe and the United States government were still getting to know each other. Prior to the 1820s, the Americans viewed the Ojibwe as a large and powerful nation. They had an uncomfortably close history with the British, who were till lurking over the border in Canada, but they otherwise inhabited a remote country unfit for white settlement. To the Ojibwe, the Americans were chimookomaan, “long knives,” in reference to the swords carried by the military officers who were the first Americans to come into their country. It was one of these long knives, Thomas McKenney, who set in motion the gathering of hundreds of paintings of Indians. Two of these showed men named Buffalo (Bizhiki).

Charles Bird King: Self portrait 1815 (Wikimedia Images)
McKenney was appointed the first Superintendent of Indian Affairs in 1824. Indian Affairs was under the Department of War at that time, and McKenneyʼs men in the West were mostly soldiers. He, like many in his day, believed that the Indian nations of North America were destined for extinction within a matter of decades. To preserve a record of these peoples, he commissioned over 100 portraits of various Indian delegates who came to Washington from all over the U.S. states and territories. Most of the painting work fell to Charles Bird King, a skilled Washington portrait artist. Beginning in 1822, King painted Indian portraits for two decades. He would paint famous men like Black Hawk, Red Jacket, Joseph Brandt, and Major Ridge, but Kingʼs primary goal was not to record the stories of important individuals so much as it was to capture the look of a vanishing race.

No-tin copied from 1824 Charles Bird King original by Henry Inman. Noodin (Wind) was a prominent chief from the St. Croix country. King’s painting of Buffalo from St. Croix was probably also copied by Inman, but its location is unknown (Wikimedia Images).
In July of 1824, William Clark, the famous companion of Meriwether Lewis, brought a delegation of Sauks, Foxes, and Ioways to Washington to negotiate land cessions. Lawrence Taliaferro, the Indian agent at Fort St. Anthony (now Minneapolis), brought representatives of the Sioux, Menominee, and Ojibwe to observe the treaty process. The St. Croix chiefs Buffalo and Noodin (Wind) represented the Ojibwe.

Charles Bird King painted portraits of most of the Indians listed here in the the 1824 Washington group by Niles’ Weekly Register, July 31, 1824. (Google Books)
The St. Croix chiefs were treated well: taken to shows, and to visit the sights of the eastern cities. However, there was a more sinister motivation behind the governmentʼs actions. McKenney made sure the chiefs saw the size and scope of the U.S. Military facilities in Washington, the unspoken message being that resistance to American expansion was impossible. This message seems to have resonated with Buffalo and Noodin of St. Croix as it is referred to repeatedly in the official record. McKenney pointed Buffalo out as a witness to American power at the Treaty of Fond du Lac (1826). Schoolcraft and Allen mention Buffalo’s trip in their own ill-fated journey up the St. Croix in 1832 (see it in this post), and Noodin talks about the soldiers he saw in Washington in the treaty deliberations in the 1837 Treaty of St. Peters.
While in Washington, Buffalo, Noodin, and most of the other Indians in the group sat with King for portraits in oil. Buffalo was shown wearing a white shirt and cloak, holding a pipe, with his face painted red. The paintings were hung in the offices of the Department of War, and the chiefs returned to their villages.
James Otto Lewis
The following summer, St. Croix Buffalo and Noodin joined chiefs from villages throughout the Ojibwe country, as well as from the Sioux, Sac and Fox, Menominee, Ho-Chunk, Ioway, Ottawa, and Potawatomi at Prairie du Chien. The Americans had called them there to sign a treaty to establish firm borders between their nations. The stated goal was to end the wars between the Sioux and Ojibwe, but it also provided the government an opportunity to assert its authority over the country and to set the stage for future land cessions.
McKenney did not attend the Treaty of Prairie du Chien leaving it to Clark and Lewis Cass to act as commissioners. A quick scan of the Ojibwe signatories shows “Pee-see- ker or buffalo, St. Croix Band,” toward the bottom. Looking up to the third signature, we see “Gitspee Waskee, or le boeuf of la pointe lake Superior,” so both the St. Croix and La Pointe Buffalos were present among the dozens of signatures. One of the government witnesses listed was an artist from Philadelphia named James Otto Lewis. Over the several days of negotiation, Lewis painted scenes of the treaty grounds as well as portraits of various chiefs. These were sent back to Washington, some were copied and improved by King or other artists, and they were added to the collection of the War Department.
The following year, 1826, McKenney himself traveled to Fond du Lac at the western end of Lake Superior to make a new treaty with the Ojibwe concerning mineral exploration on the south shore. Lewis accompanied him and continued to create images. At some point in these two years, a Lewis portrait of an Ojibwe chief named Pe-schick-ee (Bizhiki) appeared in McKenneyʼs growing War Department collection.
Lithographs
By 1830, McKenney had been dismissed from his position and turned his attention to publishing a portfolio of lithographs from the paintings in the War Department collection. Hoping to cash in his own paintings by beating McKenney to the lithograph market, Lewis released The Aboriginal Port Folio in May of 1835. It included 72 color plates, one of which was Pe-schick-ee: A Celebrated Chippeway Chief.

Pencil sketch of Pee-che-kir by Charles Bird King. King made these sketches after his original paintings to assist in making copies. (Herman J. Viola, The Indian Legacy of Charles Bird King.)
Due to financial issues The History of the Indian Tribes of North America, by McKenney with James Hall, would not come out in full release until the mid 1840s. The three-volume work became a bestseller and included color plates of 120 Indians, 95 of which are accompanied by short biographies. Most of the lithographs were derived from works by King, but some were from Lewis and other artists. Kingʼs portrait of Pee-Che-Kir: A Chippewa Chief was included among them, unfortunately without a biography. However, we know its source as the painting of the St. Croix Buffalo in 1824. Noodin and several others from that delegation also made it into lithograph form. The original War Department paintings, including both Pee-Che-Kir and Pe-schick-ee were sent to the Smithsonian, where they were destroyed in a fire in 1858. Oil copies of some of the originals, including Henry Inmanʼs copy of Kingʼs portrait of Noodin, survive, but the lithographs remain the only known versions of the Buffalo portraits other than a pencil sketch of the head of Pee-Che-Kir done by King.
The man in the Lewis lithograph is difficult to identify. The only potential clue we get from the image itself is the title of “A Celebrated Chippeway Chief,” and information that it was painted at Prairie du Chien in 1825. To many, “celebrated” would indicate Buffalo from La Pointe, but in 1825, he was largely unknown to the Americans while the St. Croix Buffalo had been to Washington. In the 1820s, La Pointe Buffaloʼs stature was nowhere near what it would become. However, he was a noted speaker from a prominent family and his signature is featured prominently in the treaty. Any assumptions about which chief was more “celebrated” are difficult.
In dress and pose, the man painted by Lewis resembles the King portrait of St. Croix Buffalo. This has caused some to claim that the Lewis is simply the original version of the King. King did copy and improve several of Lewisʼ works, but the copies tended to preserve in some degree the grotesque, almost cartoonish, facial features that are characteristic of the self-taught Lewis (see this post for another Lewis portrait). The classically-trained King painted highly realistic faces, and side-by-side comparison of the lithographs shows very little facial resemblance between Kingʼs Pee-Che-Kir and Lewisʼ Pe-schick-ee.

Thomas L. McKenney painted in 1856 by Charles Loring Elliott (Wikimedia Images)
Of the 147 War Department Indian portraits cataloged by William J. Rhees of the Smithsonian prior to the fire, 26 are described as being painted by “King from Lewis,” all of which are from 1826 or after. Most of the rest are attributed solely to King. Almost all the members of the 1824 trip to Washington are represented in the catalog. “Pee-che-ker, Buffalo, Chief of the Chippeways.” does not have an artist listed, but Noodin and several of the others from the 1824 group are listed as King, and it is safe to assume Buffalo’s should be as well. The published lithograph of Pee-che-kir was attributed solely to King, and not “King from Lewis” as others are. This further suggests that the two Buffalo lithographs are separate portraits from separate sittings, and potentially of separate chiefs.
Even without all this evidence, we can be confident that the King is not a copy of the Lewis because the King portrait was painted in 1824, and the Lewis was painted no earlier than 1825. There is, however, some debate about when the Lewis was painted. From the historical record, we know that Lewis was present at both Prairie du Chien and Fond du Lac along with both the La Pointe Buffalo and the St. Croix Buffalo. When Pe- schick-ee was released, Lewis identified it as being painted at Prairie du Chien. However, the work has also been placed at Fond du Lac.
The modern identification of Pee-che-kir as a copy of Pe-schick-ee seems to have originated with the work of James D. Horan. In his 1972 book, The McKenney-Hall Portrait Gallery of American Indians, he reproduces all the images from History of the Indian Tribes, and adds his own analysis. On page 206, he describes the King portrait of Pee-che-kir with:
“Peechekir (or Peechekor, Buffalo) was “a solid, straight formed Indian,” Colonel McKenney recalled many years after the Fond du Lac treaty where he had met the chief. Apparently the Chippewa played a minor role at the council.
Original by James Otto Lewis, Fond du Lac council, 1826, later copied in Washington by Charles Bird King.”
Presumably, the original he refers to would be the Lewis portrait of Pe-schick-ee. However, Horanʼs statement that McKenney met St. Croix Buffalo at Fond du Lac is false. As we already know, the two men met in 1824 in Washington. It is puzzling how Horan did not know this considering he includes the following account on page 68:
The first Indian to step out of the closely packed lines of stone-faced red men made McKenney feel at home; it was a chief he had met a few years before in Washington. The Indian held up his hand in a sign of peace and called out:
“Washigton [sic]… Washington… McKenney shook hands with the chief and nodded to Lewis but the artist had already started to sketch.”
McKenneyʼs original account identifies this chief as none other than St. Croix Buffalo:
In half an hour after, another band came in who commenced, as did the others, by shaking hands, followed, of course, by smoking. In this second band I recognized Pee-che-kee, or rather he recognized me–a chief who had been at Washington, and whose likeness hangs in my office there. I noticed that his eye was upon me, and that he smiled, and was busily employed speaking to an Indian who sat beside him, and no doubt about me. His first word on coming up to speak to me was, “Washington”–pointing to the east. The substance of his address was, that he was glad to see me–he felt his heart jump when he first saw me–it made him think of Washington, of his great father, of the good living he had when he visited us–how kind we all were to him, and that he should never forget any of it.
From this, Horan should have known not only that the two men knew each other, but also that a portrait of the chief (Kingʼs) already was part of the War Department collection and therefore existed before the Lewis portrait. Horanʼs description of Lewis already beginning his sketch does not appear in McKenneyʼs account and seems to invented. This is not the only instance where Horan confuses facts or takes wide license with Ojibwe history. His statement quoted above that the Ojibwe “played a minor role” in the Treaty of Fond du Lac, when they were the only Indian nation present and greatly outnumbered the Americans, should disqualify Horan from being treated as any kind of authority on the topic. However, he is not the only one to place the Lewis portrait of Pe-schick-ee at Fond du Lac rather than Prairie du Chien.
Between, 1835 and 1838 Lewis released 80 lithographs, mostly of individual Indians, in a set of ten installments. He had intended to include an eleventh with biographies. However, a dispute with the publisher prevented the final installment from coming out immediately. His London edition, released in 1844 by another publisher, included a few short biographies but none for Pe-schick-ee. Most scholars assumed that he never released the promised eleventh installment. However, one copy of a self-published 1850 pamphlet donated by Lewisʼs grandson exists in the Free Library of Philadelphia. In it are the remaining biographies. Number 30 reads:
No. 30. Pe-shisk-Kee. A Chippewa warrior from Lake Huron, noted for his attachment to the British, with whom he always sided. At the treaty held at Fond du Lac, when the Council opened, he appeared with a British medal of George the III. on his breast, and carrying a British flag, which Gen. Cass, one of the Commissioners, promptly and indignantly placed under his feet, and pointing to the stars and stripes, floating above them, informed him that that was the only one permitted to wave there.
The Chief haughtily refused to participate in the business of the Council, until, by gifts, he became partly conciliated, when he joined in their deliberations. Painted at Fond du Lac, in 1826.
This new evidence further clouds the story. Initially, this description does not seem to fit what we know about either the La Pointe or the St. Croix Buffalo, as both were born near Lake Superior and lived in Wisconsin. Both men were also inclined to be friendly toward the American government. The St. Croix Buffalo had recently been to Washington, and the La Pointe Buffalo frequently spoke of his desire for good relations with the United States in later years. It is also troubling that Lewis contradicts his earlier identification of the location of the portrait at Prairie du Chien.
It is unlikely that Pe-schick-ee depicts a third chief given that no men named Buffalo other than the two mentioned signed the Treaty of Fond du Lac, and the far-eastern bands of Ojibwe from Lake Huron were not part of treaty councils with the Lake Superior bands. One can speculate that perhaps Lewis, writing 25 years after the original painting, mistook the story of Pe-schick-ee with that one of the many other chiefs he met in his travels, but there are some suggestions that it might, in fact, be La Pointe Buffalo.
The La Pointe Band traded with the British in the other side of Lake Superior for years after the War of 1812 supposedly confirmed Chequamegon as American territory. If you’ve read this post, you’ll know that Buffalo from La Pointe was a follower of Tenskwatawa, whose brother Tecumseh fought beside the British. On July 22, 1822, Schoolcraft writes:
At that place [Chequamegon] lived, in comparatively modern times, Wabojeeg and Andaigweos, and there still lives one of their descendants in Gitchee Waishkee, the Great First-born, or, as he is familiarly called, Pezhickee, or the Buffalo, a chief decorated with British insignia. His band is estimated at one hundred and eighteen souls, of whom thirty-four are adult males, forty-one females, and forty-three children.
It’s possible that it was La Pointe Buffalo with the British flag. Archival research into the Treaty of Fond du Lac could potentially clear this up. If I stumble across any, I’ll be sure to add it here. For now, we can’t say one way or the other which Buffalo is in the Lewis portrait.
The Verdict

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe: This is Chief Buffalo from St. Croix.

Inconclusive: This could be Buffalo from La Pointe or Buffalo from St. Croix.
Sources:
Horan, James David, and Thomas Loraine McKenney. The McKenney-Hall Portrait Gallery of American Indians. New York, NY: Bramhall House, 1986. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Lewis, James O., The Aboriginal Port-Folio: A Collection of Portraits of the Most Celebrated Chiefs of the North American Indians. Philadelphia: J.O. Lewis, 1835-1838. Print.
———– Catalogue of the Indian Gallery,. New York: J.O. Lewis, 1850. Print.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal.
Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
McKenney, Thomas Loraine. Sketches of a Tour to the Lakes of the Character and Customs of the Chippeway Indians, and of Incidents Connected with the Treaty of Fond Du Lac. Baltimore: F. Lucas, Jun’r., 1827. Print.
McKenney, Thomas Loraine, and James Hall. Biographical Sketches and Anecdotes of Ninety-five of 120 Principal Chiefs from the Indian Tribes of North America. Washington: U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Indian Affairs, 1967. Print.
Moore, Robert J. Native Americans: A Portrait : The Art and Travels of Charles Bird King, George Catlin, and Karl Bodmer. New York: Stewart, Tabori & Chang, 1997. Print.
Niles, Hezekiah, William O. Niles, Jeremiah Hughes, and George Beatty, eds. “Indians.” Niles’ Weekly Register [Baltimore] 31 July 1824, Miscellaneous sec.: 363. Print.
Rhees, William J. An Account of the Smithsonian Institution. Washington: T. McGill, 1859. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Philip P. Mason. Expedition to Lake Itasca; the Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi,. [East Lansing]: Michigan State UP, 1958. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry R. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Viola, Herman J. The Indian Legacy of Charles Bird King. Washington: Smithsonian Institution, 1976. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Special thanks to Theresa Schenck of the University of Wisconsin and Charles Lippert for helping me work through this information, and to Michael Edmonds of the Wisconsin Historical Society, and Alice Cornell (formerly of the University of Cincinnati) for tracking down the single copy of the unpublished James Otto Lewis catalog.
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: Introduction
May 26, 2013
Click the question mark under the picture to see if it shows Chief Buffalo.
 ?
?
Buffalo, the 19th-century chief of the La Pointe Ojibwe, is arguably the most locally-famous person in history of the Chequamegon region. He is best known for his 1852 trip to Washington D.C., undertaken when he was thought to be over ninety years old. Buffalo looms large in the written records of the time, and makes many appearances on this website.
He is especially important to the people of Red Cliff. He is the founding father of their small community at the northern tip of Wisconsin in the sense that in the Treaty of 1854, he negotiated for Red Cliff (then called the Buffalo Estate or the Buffalo Bay Reservation) as a separate entity from the main La Pointe Band reservation at Bad River. Buffalo is a direct ancestor to several of the main families of Red Cliff, and many tribal members will proudly tell of how they connect back to him. Finally, Buffaloʼs fight to keep the Ojibwe in Wisconsin, in the face of a government that wanted to move them west, has served as an inspiration to those who try to maintain their cultural traditions and treaty rights. It is unfortunate, then, that through honest mistakes and scholarly carelessness, there is a lot of inaccurate information out there about him.
During the early twentieth century, the people of Red Cliff maintained oral traditions about about his life while the written records were largely being forgotten by mainstream historians. However, the 1960s and ʻ70s brought a renewed interest in American Indian history and the written records came back to light. With them came no fewer than seven purported images of Buffalo, some of them vouched for by such prestigious institutions as the State Historical Society of Wisconsin and the U.S. Capitol. These images, ranged from well-known lithographs produced during Buffaloʼs lifetime, to a photograph taken five years after he died, to a symbolic representation of a clan animal originally drawn on birch bark. These images continue to appear connected to Buffalo in both scholarly and mainstream works. However, there is no proof that any of them show the La Pointe chief, and there is clear evidence that several of them do not show him.
The problem this has created is not merely one of mistaken identity in pictures. To reconcile incorrect pictures with ill-fitting facts, multiple authors have attempted to create back stories where none exist, placing Buffalo where he wasnʼt, in order for the pictures to make sense. This spiral of compounding misinformation has begun to obscure the legacy of this important man, and therefore, this study attempts to sort it out.
Bizhikiwag
The confusion over the images stems from the fact that there was more than one Ojibwe leader in the mid-nineteenth century named Bizhiki (Buffalo). Because Ojibwe names are descriptive, and often come from dreams, visions, or life experiences, one can be lead to believe that each name was wholly unique. However, this is not the case. Names were frequently repeated within families or even outside of families. Waabojiig (White Fisher) and Bugone-Giizhig (Hole in the Day) are prominent examples of names from Buffaloʼs lifetime that were given to unrelated men from different villages and clans. Buffalo himself carried two names, neither of which was particularly unique. Whites usually referred to him as Buffalo, Great Buffalo, or LaBoeuf, translations of his name Bizhiki. In Ojibwe, he is just as often recorded by the name Gichi-Weshkii. Weshkii, literally “new one,” was a name often given to firstborn sons in Ojibwe families. Gichi is a prefix meaning “big” or “great,” both of which could be used to describe Buffalo.

Nichols and Nyholm translate Bizhiki (Besheke, Peezhickee, Bezhike, etc.) as both “cow” and “buffalo.” Originally it meant “buffalo” in Ojibwe. As cattle became more common in Ojibwe country, the term expanded to include both animals to the point where the primary meaning of the word today is “cow” in some dialects. These dialects will use Mashkodebizhiki (Prairie Cow) to mean buffalo. However, this term is a more recent addition to the language and was not used by individuals named Buffalo in the mid- nineteenth century. (National Park Service photo)
One glance at the 1837 Treaty of St. Peters shows three Buffalos. Pe-zhe-kins (Bizhikiins) or “Young Buffalo” signed as a warrior from Leech Lake. “Pe-zhe-ke, or the Buffalo” was the first chief to sign from the St. Croix region. Finally, the familiar Buffalo is listed as the first name under those from La Pointe on Lake Superior. It is these two other Buffalos, from St. Croix and Leech Lake, whose faces grace several of the images supposedly showing Buffalo of La Pointe. All three of these men were chiefs, all three were Ojibwe, and all three represented their people in Washington D.C. Because they share a name, their histories have unfortunately been mashed together.
Who were these three men?

Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Dagwagaane (Ta-qua-ga-na), check out the People Index.
The familiar Buffalo was born at La Pointe in the middle of the 18th century. He was a member of the Loon Clan, which had become a chiefly clan under the leadership of his grandfather Andeg-wiiyas (Crowʼs Meat). Although he was already elderly by the time the Lake Superior Ojibwe entered into their treaty relationship with the United States, his skills as an orator were such that by the Treaty of 1854, one year before his death, Buffalo was the most influential leader not only of La Pointe, but of the whole Lake Superior country.
Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Gaa-bimabi (Ka-be-ma-be), check out the People Index.
William Warren, describes the St. Croix Buffalo as a member of the Bear Clan who originally came to the St. Croix from Sault Ste. Marie after committing a murder. He goes on to declare that this Buffaloʼs chieftainship came only as a reward from traders who appreciated his trapping skills. Warren does admit, however, that Buffaloʼs influence grew and surpassed that of the hereditary St. Croix leaders.

Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Flat Mouth, check out the People Index.
The “Young Buffalo,” of the Pillager or Leech Lake Ojibwe of northern Minnesota was a war chief who also belonged to the Bear Clan and was considerably younger than the other two Buffalos (the La Pointe and St. Croix chiefs were about the same age). As Biizhikiins grew into his later adulthood, he was known simply as Bizhiki (Buffalo). His mark on history came largely after the La Pointe Buffaloʼs death, during the politics surrounding the various Ojibwe treaties in Minnesota and in the events surrounding the US-Dakota War of 1862.
The Picture Search
In the coming months, I will devote several posts to analyzing the reported images of Chief Buffalo that I am aware of. The first post on this site can be considered the first in the series. Keep checking back for more.
Sources:
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Nichols, John, and Earl Nyholm. A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 1995. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry R. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Treuer, Anton. The Assassination of Hole in the Day. St. Paul, MN: Borealis, 2010. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
…a donation of twenty-four sections of land covering the graves of our fathers, our sugar orchards, and our rice lakes and rivers…
March 29, 2013

Symbolic Petition of Chippewa Chiefs: Original birch bark petition of Oshkaabewis copied by Seth Eastman and printed in “Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States” by Henry Rowe Schoolcraft (1851). Digitized by University of Wisconsin Libraries Wisconsin Electronic Reader project (1998).
For the first post on Chequamegon History, I thought I’d share my research into an image that has been circulating around the area for several years now. The image shows seven Ojibwe chiefs by their doodemag (clan symbols), connected by heart and mind to Lake Superior and to some smaller lakes. The clans shown are the Crane, Marten, Bear, Merman, and Bullhead.
All the interpretations I’ve heard agree that this image is a copy of a birch bark pictograph, and that it represents a unity among the several chiefs and their clans against Government efforts to remove the Lake Superior bands to Minnesota.
While there is this agreement on the why question of this petition’s creation, the who and when have been a source of confusion. Much of this confusion stems from efforts to connect this image to the famous La Pointe chief, Buffalo (Bizhiki/Gichi-weshkii).
In 2007, the Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission (GLIFWC) released the short documentary Mikwendaagoziwag: They Are Remembered. While otherwise a very good overview of the Lake Superior Ojibwe in this era, it incorrectly uses this image to describe Buffalo going to Washington D.C. in 1849. Buffalo is famous for a trip to Washington in 1852, but he was not part of the 1849 group.
At the time the GLIFWC film was released, the Wisconsin Historical Society website referred to this pictograph as, “Chief Buffaloʼs Petition to the President,” and identified the crane as Buffalo. Citing oral history from Lac Courte Oreilles, the Society dated the petition after the botched 1850-51 removal to Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in hundreds of Ojibwe deaths from disease and starvation due to negligence, greed, and institutional racism on the part of government officials. The Historical Society has since revised its description to re-date the pictograph at 1848-49, but it still incorrectly lists Buffalo, a member of the Loon Clan, as being depicted by the crane. The Sandy Lake Tragedy, has deservedly gained coverage by historians in recent years, but the pictographic petition came earlier and was not part of it.
If the Historical Society had contacted Chief Buffaloʼs descendants in Red Cliff, they would have known that Buffalo was from the Loon Clan. The relationship between the Loons and the Cranes, as far as which clan can claim the hereditary chieftainship of the La Pointe Band, is very interesting and covered extensively in Warrenʼs History of the Ojibwe People. It would make a good subject for a future post.
After looking into the history of this image, I can confidently say that Buffalo is not one of the chiefs represented. It was created before Sandy Lake and Buffalo’s journey, but it is related to those events. Here is the story:
In late 1848, a group of Ojibwe chiefs went to Washington. They wanted to meet directly with President James K. Polk to ask for a permanent reservations in Wisconsin and Michigan. At that time the Ojibwe did not hold title to any part of the newly-created state of Wisconsin or Upper Michigan, having ceded these lands in the treaties in 1837 and 1842. In signing the treaties, they had received guarantees that they could stay in their traditional villages and hunt, fish, and gather throughout the ceded territory. However, by 1848, rumors were flying of removal of all Ojibwe to unceded lands on the Mississippi River in Minnesota Territory. These chiefs were trying to stop that from happening.
John Baptist Martell, a mix-blood, acted as their guide and interpreter. The government officials and Indian agents in the west were the ones actively promoting removal, so they did not grant permission (or travel money) for the trip. The chiefs had to pay their way as they went by putting themselves on display and dancing as they went from town to town.
Martell was accused by government officials of acting out of self interest, but the written petition presented to congress asked for, “a donation of twenty-four sections of land covering the graves of our fathers, our sugar orchards, and our rice lakes and rivers, at seven different places now occupied by us at villages…” The chiefs claimed to be acting on behalf of the chiefs of all the Lake Superior bands, and there is reason to believe them given that their request is precisely what Chief Buffalo and other leaders continued to ask for up until the Treaty of 1854.

This written petition accompanied the pictographic petitions. It clearly states the goal of the the chiefs was to secure permanent reservations around the traditional villages east of the Mississippi.
The visiting Ojibwes made a big impression on the nationʼs capital and positive accounts of the chiefs, their families, and their interpreter appeared in the magazines of the day. Congress granted them $6000 for their expenses, which according to their critics was a scheme by Martell. However, it is likely they were vilified by government officials for working outside the colonial structure and for trying to stop the removal rather than for any ill-intentions of the part of their interpreter. A full scholarly study of the 1848-49 trip remains to be done, however.

Amid articles on the end of the slave trade, the California Gold Rush, and the benefits of the “passing away of the Celt” during the Great Irish Famine, two articles appeared in Littell’s Living Age magazine about the 1849 delegation. The first is tragic, and the second is comical.
Along with written letters and petitions supporting the Ojibwe cause, the chiefs carried not only the one, but several birchbark pictographs. The pictographs show the clan animals of several chiefs and leading men from several small villages from the mouth of the Ontonagon River to Lac Vieux Desert in Upper Michigan and smaller satellite communities in Wisconsin. After seeing these petitions, the artist Seth Eastman copied them on paper and gave them to Henry Schoolcraft who printed and explained them alongside his criticism of the trip. They appear in his 1851 Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States.

Kenisteno, and his Band of Trout Lake, Wisconsin

Okundekund, and his Band of Ontonagon, Michigan (Upper) Kakake-ogwunaosh, and his Band of the head of Wisconsin River (Lower)
According to Schoolcraft, the crane in the most famous pictograph is Oshkaabewis, a Crane-clan chief from Lac Vieux Desert, and the leader of the 1848-49 expedition. In the Treaty of 1854, he is listed as a first chief from Lac du Flambeau in nearby Wisconsin. It makes sense that someone named Oshkaabewis would lead a delegation since the word oshkaabewis is used to describe someone who carries messages and pipes for a civil chief.

Kaizheosh [Gezhiiyaash], and his band from Lake Vieu Desert, Michigan and Wisconsin (University of Nebraska Libraries)
Long Story Short…
This is not Chief Buffalo or anyone from the La Pointe Band, and it was created before the Sandy Lake Tragedy. However it is totally appropriate to use the image in connection with those topics because it was all part of the efforts of the Lake Superior Ojibwe to resist removal in the late 1840s and early 1850s. However, when you do, please remember to credit the Lac Vieux Desert/Ontonagon chiefs who created these remarkable documents.






















